However, if liabilities are more than assets, you need to look more closely at the company’s ability to pay its debt obligations. Both revenue and retained earnings are crucial for assessing a company’s financial health, but they represent different aspects of the financial picture. Revenue is the income generated by a company before deducting operating expenses and overhead costs.
- Liabilities are classified as current liabilities or long-term liabilities.
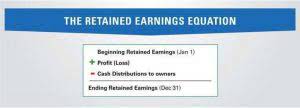
- Retained earnings represent a company’s accumulated profits or losses.
- When the retained earnings balance is less than zero, it is referred to as an accumulated deficit.
- For example, management might decide to build up a cash reserve, repay debt, fund strategic investment projects or pay dividends to shareholders.
- While they may seem similar, the current portion of long-term debt is specifically the portion due within this year of a piece of debt that has a maturity of more than one year.
- Additionally, investors may prefer to see larger dividends rather than significant annual increases to retained earnings.
- Looking at retained earnings can be useful, but they’re more valuable when observed over a longer period of time.
Why does total liabilities and equity equal total assets?
Because of their higher costs and longevity, assets are not expensed, but depreciated, or «written off» over a number of years according to one of several depreciation schedules. Assets can be defined as objects or entities, both tangible and intangible, that the company owns that have economic value to the business. Now let’s look a closer look at each of these basic elements of accounting. In this Accounting Basics tutorial I discuss the five account types in the Chart of Accounts.
Significance of retained earnings in attracting venture capital

Over the same duration, its stock price rose by $84 ($227 – $143) per share. Revenue is the money generated by a company during a period, but before operating expenses and overhead costs are deducted. In some industries, revenue is called gross sales because the gross figure is calculated QuickBooks ProAdvisor before any deductions.
Why are retained earnings important for small business owners?
Retained earnings represent a useful link between the income statement and the balance sheet, as they are recorded under shareholders’ equity, which connects the two statements. This reinvestment into the company aims to achieve even more earnings in the future. However, it can be challenged by the shareholders through a majority vote because they are the real owners of the company. Retained earnings are also called earnings surplus and represent reserve money, which is available to company management for reinvesting retained earnings normal balance back into the business. When expressed as a percentage of total earnings, it is also called the retention ratio and is equal to (1 – the dividend payout ratio). Shareholders all get cash dividends if you issue cash dividends, for example.
- We’ll now move to a modeling exercise, which you can access by filling out the form below.
- At the heart of it, the balance sheet is a document that shows the financial condition of a company over time.
- Retained earnings accumulate all profits and losses from when a company starts operating.
- Changes in balance sheet accounts are also used to calculate cash flow in the cash flow statement.
- Examples of expenses are office supplies, utilities, rent, entertainment, and travel.
- Retained earnings are a type of equity and are therefore reported in the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet.
- And while that seems like a lot to have available during your accounting cycles, it’s not.
Usually, these include special dividends that differ from the year-end allotments. Stockholders’ equity is a measurement of the general financial health of the company. If the number for stockholders’ equity is negative, it may warn of impending bankruptcy (particularly if it is due to a high debt load). When a large amount of cash is recorded on the balance sheet, it’s generally a good sign as it offers protection during business slow-downs and provides options for future growth. The balance sheet highlights the financial position of a company at a particular point in time (generally the last day of its fiscal year).
Are you still wondering about calculating and interpreting retained earnings? Upon combining the three line items, we arrive at the end-of-period balance – for instance, Year 0’s ending balance is $240m. A unique type of Expense account, Depreciation Expense, is used when purchasing Fixed Assets. Costly items, such as vehicles, equipment, and computer systems, are not expensed, but are depreciated or written off over the life expectancy of the item. If I purchase a $30,000 vehicle (asset) with a $25,000 loan (liability) and $5,000 in cash (equity), I’ve acquired an asset of $30,000, but have only $5,000 of equity in the asset. Examples of liability accounts that display on the Balance Sheet include Accounts Payable, Sales Tax Payable, Payroll Liabilities, and Notes Payable.
- If you don’t pay dividends, you can ignore this part and substitute $0 for this portion of the retained earnings formula.
- Retained earnings refer to the historical profits earned by a company, minus any dividends it paid in the past.
- Retained earnings being low indicates that much of the company’s profits are paid out to shareholders in dividends.
- The confusion often arises because retained earnings represent reinvested profits.
- Also known as the Profit and Loss report, this report subtracts expenses from revenue to determine the net profit of a business.
- If your business is seasonal, like lawn care or snow removal, your retained earnings may fluctuate substantially from one quarter to the next.
- Retained earnings also act as an internal source of finance for most companies.
In some industries, it’s referred to as gross sales because it’s calculated before deductions. How can you see a snapshot of your business’ financial situation at any time? This special report tells you about the things your business owns and what it owes to others, as well as how much value your business has for its owners. One key thing to pay attention to is the amount of money your company keeps for future use, which can show how stable your business is and how much it might grow. Also, keep in mind that the equation you use to get shareholders’ equity is the same you use to get your working capital. Working capital is the value of all your assets, minus liabilities.
The balance sheet outlines all of the assets, equity, and liability of an organization. At the heart of it, the balance sheet is a document that shows the financial condition of a company over time. Here’s an example of a standard T-account for a business showing debits on the left side (the debit side) and credits on the right side (the credit side). Although each account has a normal balance in practice it is possible for any account to have either a debit or a credit balance depending on the bookkeeping entries made. For this reason the account balance for items on the left hand side of the equation is normally a debit and the account balance for items on the right side of the equation is normally a credit. Shareholders of Apple Inc. approve the dividend declared by the board of directors bookkeeping amounting to 100,000.

This essentially refers to the business’ net profit generated during the period, after subtracting business expenses from your revenue. Current assets are items that are completely consumed, sold, or converted into cash in 12 months or less. Examples of current assets include accounts receivable and prepaid expenses. If your business is seasonal, like lawn care or snow removal, your retained earnings may fluctuate substantially from one quarter to the next. Therefore, the calculation may fail to deliver a complete picture of your finances.The other key disadvantage occurs when your retained earnings are too high. Excessively high retained earnings can indicate your business isn’t spending efficiently or reinvesting enough in growth, which is why performing frequent bank reconciliations is important.
Care must be taken to stay in compliance with these agreements. Unless a lender waives a ratio-based covenant violation, it can result in penalties, higher interest rates or even default. Below is a short video explanation to help you understand the importance of retained earnings from an accounting perspective. All of the other options retain the earnings for use within the business, and such investments and funding retained earnings on balance sheet activities constitute retained earnings.